Modern infrastructure’s lifelines are its pipelines, which make it possible to transmit essential commodities like water, oil, and gas. The longevity and effectiveness of pipelines must be ensured in the context of pipeline infrastructure.
The joint connections between them greatly aid the pipes’ structural integrity and leak prevention. This is where pipe joint coating enters the picture, offering a shield that increases toughness and shields against pipeline corrosion.
It is vital to remember that pipe joint coating methods can change depending on the type of pipeline, the environment, and the project needs. But this blog will act as a starting point, giving readers a broad overview of the procedure and the information they need to delve deeper.
Read out: “Internal Corrosion in Gas Pipelines”
What Exactly is a Pipe Joint?
The field junction is where two pipe spools or pipe joints are welded together. This is a crucial location because the pipe is welded here and has an uncoated surface. The field joint is hence exposed to the environment and vulnerable to corrosion.
Due to compatibility concerns between the factory-applied or mainline coating and the chosen substance used to protect the field joint, field joints are frequently considered the weakest point in a pipeline.
Step By Step Procedure Of Pipe Joint Coating
Following are some easy steps of procedure of pipe joint coating:
Surface Cleaning
Cleaning the joint to eliminate debris, oil, or other pollutants hindering the coating’s adhesion is a common step in surface preparation. The surface may also be gently roughened to enhance coating adhesion during surface preparation.
Masking
Masking Tape or other suitable materials in pipe joint are used to block off any regions that need not be coated, such as threads or specific areas of joints. This ensures that the coating only gets applied to the regions that need it.
Priming (optional)
Before the coating, a primer may, in some circumstances, be applied to the surface. The primer enhances corrosion resistance and adhesion. The specific coating technique and the kind of pipes being linked will determine the primer utilized.
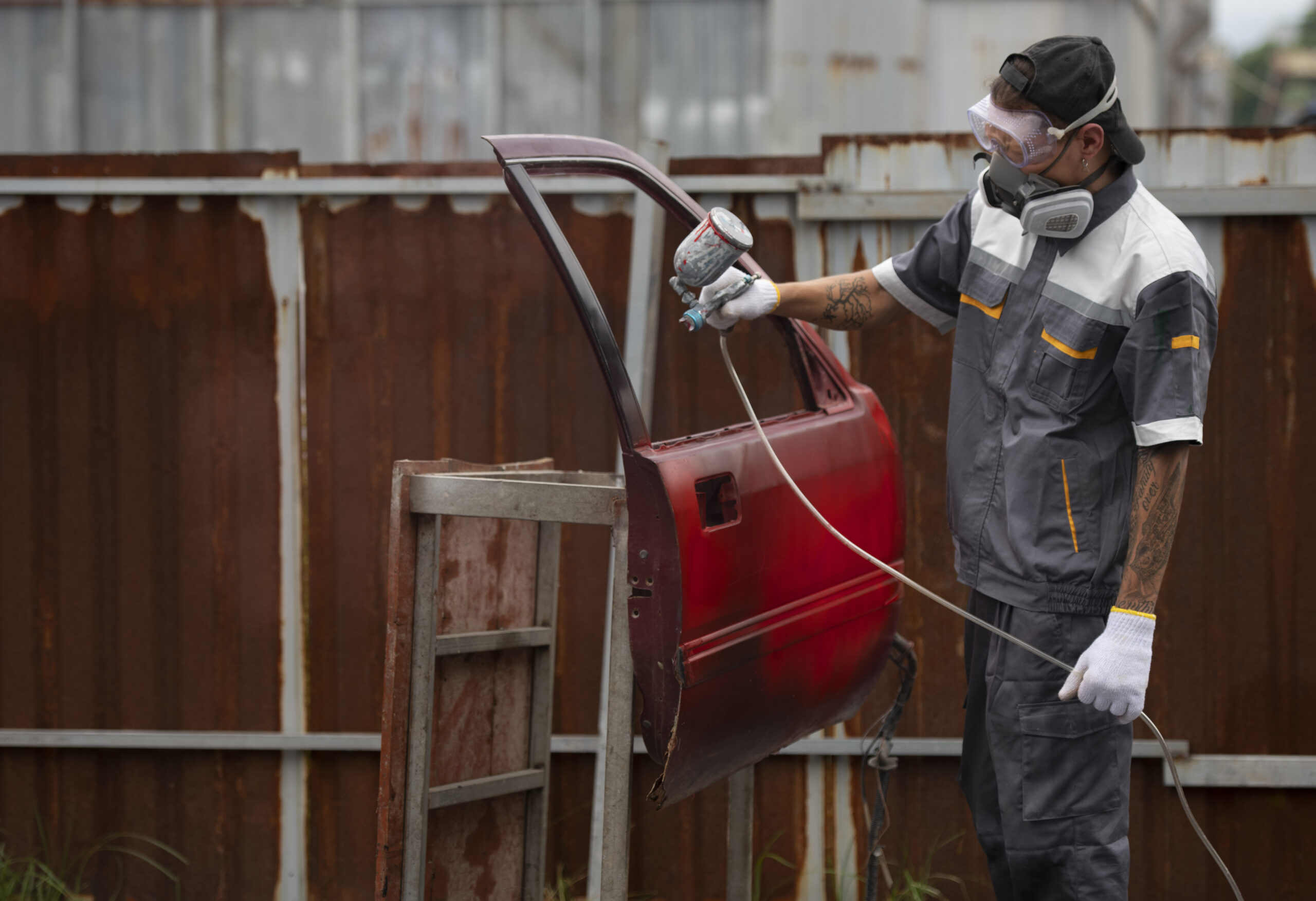
Application of Coatings
Depending on the precise needs, the coating material may change, but popular coating types include epoxy, polyurethane, or other corrosion-resistant substances. The coating is evenly applied to the joint using brushes, rollers, or spray equipment.
It can be necessary to apply several coats, and between each coat, the previous one needs to dry or cure by the manufacturer’s directions. You can use our Joint Lock Ring to tightly join your pipeline system.
Curing
The coating must cure or dry after application. Depending on the coating, the procedure may require heat curing, air drying, or mixing the two. For optimum performance, the coating manufacturer should use the curing time and temperature as indicated.
Examination and Quality Control
Quality control tests are frequently performed on pipe joint coatings to guarantee their efficacy and longevity. These examinations could include adhesion tests, thickness measures, holiday (pinhole) detection, or other examinations mandated by project specifications or industry standards.
Protection and Installation of pipe joint
After passing the quality control tests, the coated pipe joints are put in the pipeline system. The coating should be handled carefully and protected from harm during transit, storage, and installation.
Advantages Of Pipe Joint Coating
Improved Structure
Pipe joint coatings strengthen the joint’s resistance to external stresses. Coatings strengthen and stiffen joints, preventing distortion, cracking, and leaking. In high-pressure, temperature-variable, or mechanical-stress applications, this is crucial.
Leak Prevention
Pipe joint coatings seal fluids and glasses, preventing leaks and environmental concerns. Leaks can seriously affect oil and gas, water delivery, and chemical production.
Cost savings
Coating may cost more upfront, but it can save money over time. Coated pipe joints last longer, need fewer repairs, and have lower maintenance and replacement costs.
Simple Setup and Maintenance
Applying pipe joint coatings during production or externally is easy. Coated joints are easier to clean and maintain, lowering operational costs.
Aesthetics
Pipe joint coatings also make pipes look better. This can benefit architectural or ornamental projects with exposed pipes.
What Differentiates Mainline Coating from Pipe Joint Coating?
Field joint coating must ensure adhesion between the mainline coating and the field joint coating, whereas mainline coating must ensure adherence exclusively to the pipe surface. Mainline coatings are done at the factory, with fewer time limitations, making it easier to maintain quality.
On the other hand, pipe joints are applied on the job site, with time limits and the need to finish the coating rapidly. While field joint coatings must be applied in harsh environmental conditions, mainline coatings can be simply applied in production settings.
Selecting The Right Coating
Numerous elements must be considered when designing and choosing the best pipeline coating.
The diameter of the pipe, the service pressures or operating temperatures of the transport materials, the soil conditions if installing a landline, the installation techniques, cathodic protection (CP), and whether impressed current CP or sacrificial CP will be used are just a few of the crucial factors that need to be carefully analyzed.
All of these variables will affect the choice of material for pipeline protection.
Conclusion
During the coating procedure of pipe joint coating, several crucial steps are required to ensure the coating’s efficacy and durability. The procedure begins with thoroughly preparing surfaces, including cleaning and removing contamination. A primer is then applied to enhance adhesion and prevent corrosion. Following the given steps guarantees a corrosion-resistant pipe joint that can withstand the demands of its intended application.
FAQs
What materials are employed in pipe coating?
The most often used materials for pipe coating are bituminous coatings, resins, paints, waxes, oils, varnishes, lacquers, plasticizers, greases, plastics including polyurethane, Rilsan, polyethylene, PTFE, and PVC, elastomers, vitreous enamel, and cement mortar.
What is the main reason for using joint coating?
The place where two pipeline sections meet and are welded together is known as a field joint. To prevent corrosion of the bare steel region, anti-corrosion coatings must be applied here.
What is the coating’s principle?
The film or cloth carries a certain amount of the adhesive solution. The extra glue is peeled off in the prepared gap beneath the fixed Mayer bar. Extremely diverse coating materials can be coated using this technique with a very flexible application weight.
How is the thickness of a coating gauged?
Coatings on nonmetallic substrates can be measured for thickness using ultrasonic paint thickness gauges. An ultrasonic transducer built within the paint meter’s probe sends a pulse through the coating. The pulse is transformed into a high-frequency electrical signal when it bounces from the substrate to the transducer.
What is the difference between pipe lining and pipe coating?
Pipe lining involves inserting a new inner layer to repair pipes internally, while pipe coating applies a protective layer to the pipe’s exterior to prevent corrosion and damage. Learn in detail.